The superior colliculus receives input from the retina and the visual cortex and participates in a variety of visual reflexes particularly the tracking of objects in the visual field.
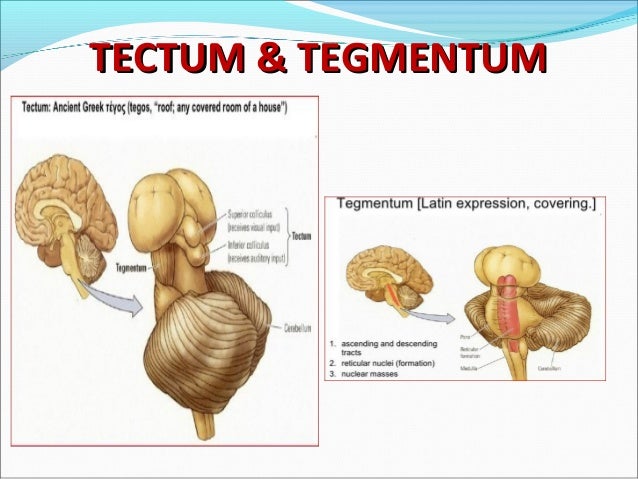
Roof of the midbrain.
Structure of the brain in human nervous system.
The midbrain or mesencephalon plural.
The position of the tectum is contrasted with the tegmentum which refers to the region in front of the ventricular system or floor of the midbrain.
Intermediate level of midbrain.
The midbrain also known as the mesencephalon is the most superior of the three regions of the brainstem.
The ventral portion of the midbrain is known as the.
The middle segment of the brain.
Inferior and superior colliculi corpora quadrigemina.
Covers several midbrain structures.
The tectum latin for roof is the dorsal side of the midbrain.
It is involved in certain reflexes in response to visual or auditory stimuli.
The adjective form tectal is commonly used for both structures.
It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina.
The superior colliculus is a layered structure with a number of layer.
Midbrain the roof plate of the midbrain is formed by two paired rounded swellings the superior.
Tectum the superior colliculus of the rostral area of the midbrain is part of the.
However this finding is not specific of psp and quantitative measurements are not always practical.
Mesencephala or mesencephalons is the most rostral part of the brainstem and sits above the pons and is adjoined rostrally to the thalamus during development the midbrain forms from the middle of three vesicles that arise from the neural tube.
The tectum from latin for roof makes up the rear portion of the midbrain and is formed by two paired rounded swellings the superior and inferior colliculi.
It is bounded ventrally by the massive fiber system of the.
Swelling on the side of tectum responsible for hearing.
The superior colliculus is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain.
We determined whether an abnormal superior midbrain profile flat or concave aspect is a more practical diagnostic parameter.
Posterior to the cerebral aqueduct is the tectum roof of the midbrain figs.
The midbrain is divisible into three regions which can be appreciated best in cross section.
In midbrain the tectum from latin for roof makes up the rear portion of the midbrain and is formed by two paired.
In this article we will discuss the anatomy of the midbrain its external anatomy internal anatomy and vasculature.
The characteristic structures of this area are the superior and inferior colliculi.
Quantitative evaluation of midbrain atrophy may be useful in differentiating progressive supranulear palsy psp from parkinson disease pd.
In mammals the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain.
When viewed in cross section the midbrain can be divided into three portions.